
Antireflection Coatings for Space Applications
P. Kupinski and J. Watson
I. Introduction
In Space applications, optical coatings can be exposed to vacuum, extreme temperatures, high intensity radiation and ionized gas. In the course of providing optics and coatings for Space applications, Optimax has been involved in several rounds of qualification testing. The following is a brief description of the tests performed for these programs.
II. Facility and Process
All Optimax coating operations are performed in a cleanroom. Optics are cleaned prior to coating in Class 1000 room under Class 100 benches. The cleaning and coating processes used have demonstrated performance on thousands of surfaces in high energy laser applications. Optimax coats optics using reactive evaporation and plasma ion assisted deposition (PIAD). Coatings for Space applications are always applied in clean, cryogenically pumped chambers. The coatings tested in this report were deposited using reactive evaporation. The processes used were tailored to provide high purity films (<3ppm absorption at 1064nm) that are spectrally stable as both a function of time and environment.
III. Spectral Stability
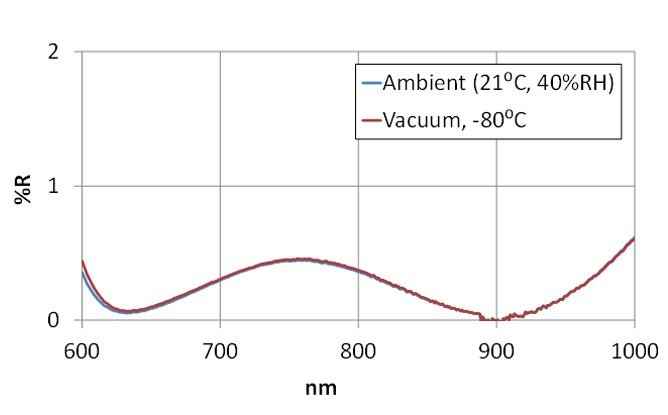
Broadband AR coatings were tested for change in performance when exposed to vacuum and ‐80⁰C. Testing was performed on six different coated glass types1 by an independent laboratory (Spica Technologies, Inc.). None of the AR coatings tested showed a significant change in spectral performance when moved from ambient to simulated Space vacuum (Figure 1):
IV. Radiation Exposure
In two separate tests Optimax AR coatings were subjected to high doses of gamma radiation using a Co 60 source. The first test was performed by Aeroflex RAD with a cumulative dose of 30kRad. The coating showed no loss in transmission (+/‐0.1%T) from 350 to 1000nm. On a second program Optimax AR coatings were tested up to 2MRad of cumulative dose by the University of Arizona. Again the coatings showed no significant loss in transmission (+/‐0.1%T) when tested over the visible spectrum.
V. Durability
BBAR coatings on the six different glass types listed in Section III passed the following tests (in order of testing):
All testing done to MIL‐C‐48497A
- Adhesion (tape test from edge)
- Humidity (24hrs at 49⁰F, 98%RH)
- Abrasion (50 rubs, cheesecloth, 9PSI) and Adhesion again
- Temp (5cycles, ‐26⁰C, 71⁰C, 2hr soak)
*5x MIL SPEC requirement - Solubility and Cleanability
- No observable change in %T after tests 1‐5.
The coatings also survived repeated cycling to ‐80⁰C/vacuum during spectral testing at Spica without change in mechanical or spectral integrity. Coatings applied with the processes used for Space applications routinely pass Severe Abrasion requirements of MIL‐C‐48987A (although it wasn’t required for this test).
VI. Conclusion
Optimax AR coatings performed well in testing meant to simulate both low earth orbit and deeper Space applications. The coatings also passed tests meant to simulate storage and handling in high humidity environments prior to launch. At a minimum, all Optimax coatings destined for Space are tested spectrally at 0%RH and 40%RH to insure stable spectral performance in ground testing and in use. Other testing can be provided at the customer’s request.